How does chronic prostatitis affect male sexual function?
Chronic prostatitis is a common urogenital system disease in men, which severely affects their physical and mental health. It may lead to discomfort such as perineal distension and pain, frequent urination, urgency, and other urinary symptoms, and can also impact male sexual function. Many may wonder how chronic prostatitis affects male sexual function, and here is a scientific explanation.
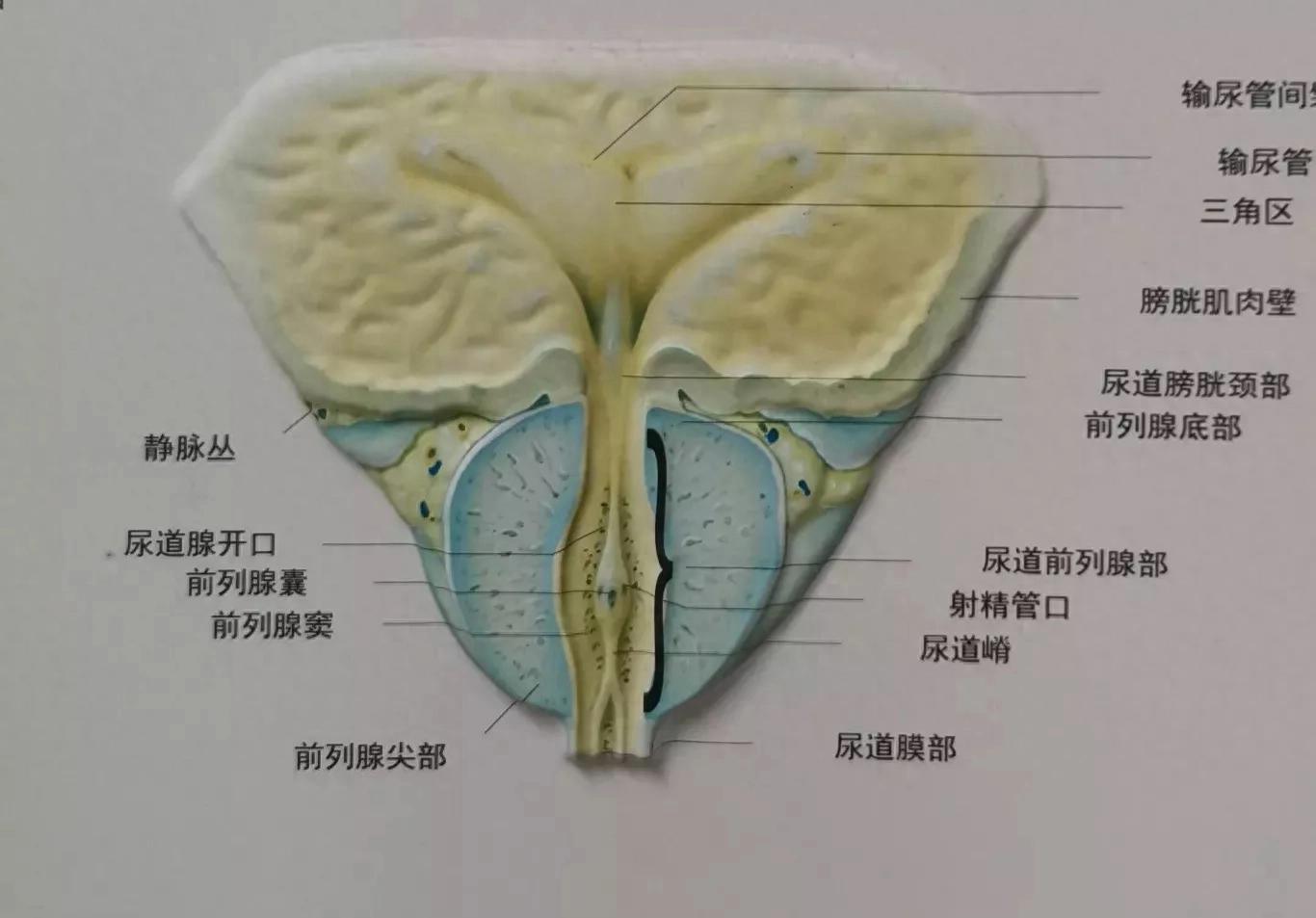
Chronic prostatitis is an inflammatory disease. The prostate is primarily composed of glandular tissue, and prostatitis essentially involves an inflammatory response in this tissue. Under the influence of inflammation, the sensitivity of local nerves in men may become abnormal, leading to a potential decrease in sexual arousal and ejaculation thresholds. Inflammatory mediators can stimulate the nerve tissues within the prostate, resulting in reduced excitability.
Chronic prostatitis is also a process of chronic congestion. Prolonged congestion and tissue edema in the prostate can impair male ejaculatory function, particularly affecting ejaculation timing. If the ejaculation threshold is lowered, it may lead to premature ejaculation.
Chronic prostatitis may cause pain and discomfort in the pelvic region, including the lower abdomen, perineum, lumbosacral area, groin, scrotum, and testicles. In some cases, it can even lead to painful ejaculation. These negative pain experiences can result in decreased libido in men, and in severe cases, may contribute to erectile dysfunction or premature ejaculation. Psychogenic factors are often the primary cause of erectile dysfunction induced by pain.
Chronic prostatitis is a condition prone to recurrence, often accompanied by prolonged symptomatic and treatment cycles, which inevitably challenges men's psychological well-being. Many men experience severe anxiety and depression as a result, and in some cases, medication is required to manage these psychological states. Anxiety and depression significantly impact male libido and erectile function.
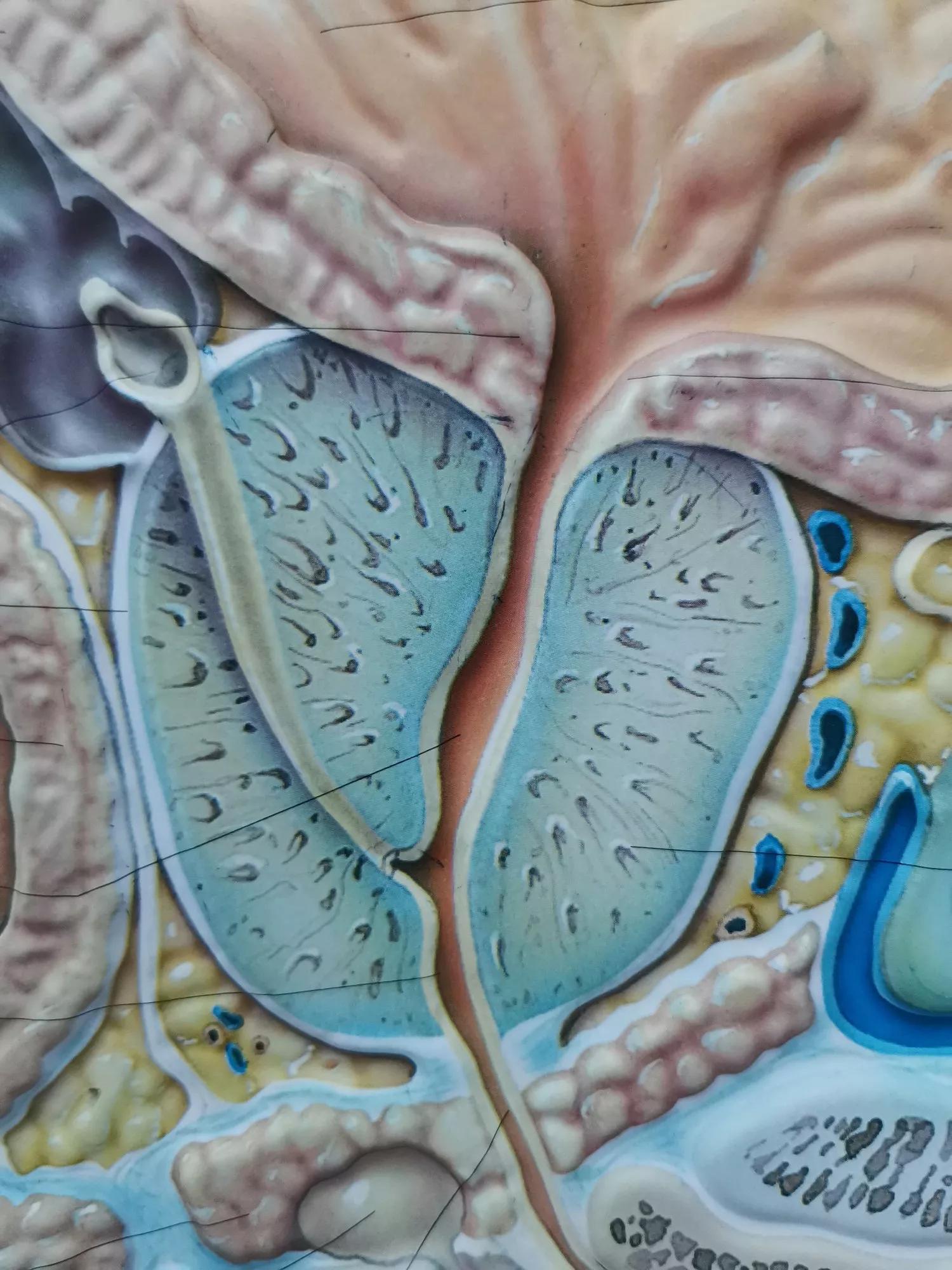
Therefore, the impact of chronic prostatitis on male sexual function is multifaceted, involving neurological, vascular, and psychological factors.