A ready-to-build muscle strength training program for kids
Muscle strength refers to the ability of a muscle or muscle group to overcome resistance and create tension. It is the basis of the body's athletic ability and an important indicator of metabolic health.
With the popularity of electronic devices, increased sedentary time and lack of physical activity in adolescents can lead to weakened muscle strength in adolescents.
What are the possible dangers of insufficient muscle strength? How can we help teenagers scientifically improve muscle strength? Today we will answer these questions and provide an exercise plan for teenagers.

The possible harm of insufficient muscle strength
Maintaining adequate muscle strength in adolescents is essential for promoting physical and mental health development, as well as reducing various short- and long-term health risks. Insufficient muscle strength can cause the following harms to adolescents.
1 Short-term impact
Rounded shoulders, hunched back Weakness of the core muscles leads to poor spinal stability and affects posture.
Increased risk of sports injuries Weakened muscle strength can make teens more prone to sprains, strains, and other injuries during sports or daily activities. Weakened muscle strength can also affect adolescents' athletic abilities, limiting their participation in physical activities.
Decreased endurance Adolescents with poor muscular endurance are more likely to fatigue during sports tests such as long-distance running.
2 Long-term health risks
Increased cardiovascular and metabolic problems Decreased muscle mass directly reduces basal metabolic rate and increases the risk of metabolic problems such as insulin resistance and fatty liver disease in adolescence.
Decreased bone density Weakening muscle strength may have an impact on bone density, increasing the risk of osteoporosis later in life.
Increased risk of obesity People with low muscle mass have a lower basal metabolic rate and are more likely to store fat, forming "hidden obesity" (normal weight but high body fat percentage).
Poor posture caused by decreased muscle strength may make neck, shoulder, low back pain more common in adolescents.
In addition, low physical fitness and body image concerns due to weakened muscle strength can also have an impact on mental health and can lead to feelings of anxiety or depression. Adolescents with poor muscle strength may perform poorly in physical education classes and group activities, leading to a lack of self-confidence and even social avoidance.
Scientifically improve muscle strength to do so
Muscle strength training for adolescents should follow the following principles.
Full supervision All training sessions should be supervised by qualified coaches who understand the principles of resistance training for teenagers.
Technique First Focus on practicing technique correctly before increasing resistance or repetitions. Start with no load until you master the movement.
Safety first Avoid heavy weight training, focusing on bodyweight training and light equipment.
Gradually increase resistance and repetitions as strength and skill improve.
All-round development Taking into account the training of upper limbs, lower limbs, and core muscles.
Increase fun Combine games, challenges and other methods to increase the interest of young people in participating.
Persistence Muscle growth requires continuous stimulation and recovery, and regular exercise is key.

For muscle strength training for teenagers, it is recommended to practice the following.
Upper limb training Push-ups (knees can be on the ground), elastic band rowing.
Lower limb training Squats, lunge squats, deadlifts, etc.
Core training Plank (30 seconds ~ 1 minute), supine crunches.
Full body coordination training Step jumping, burpee jumping, skipping rope, etc.
Muscle strength training program for teenagers
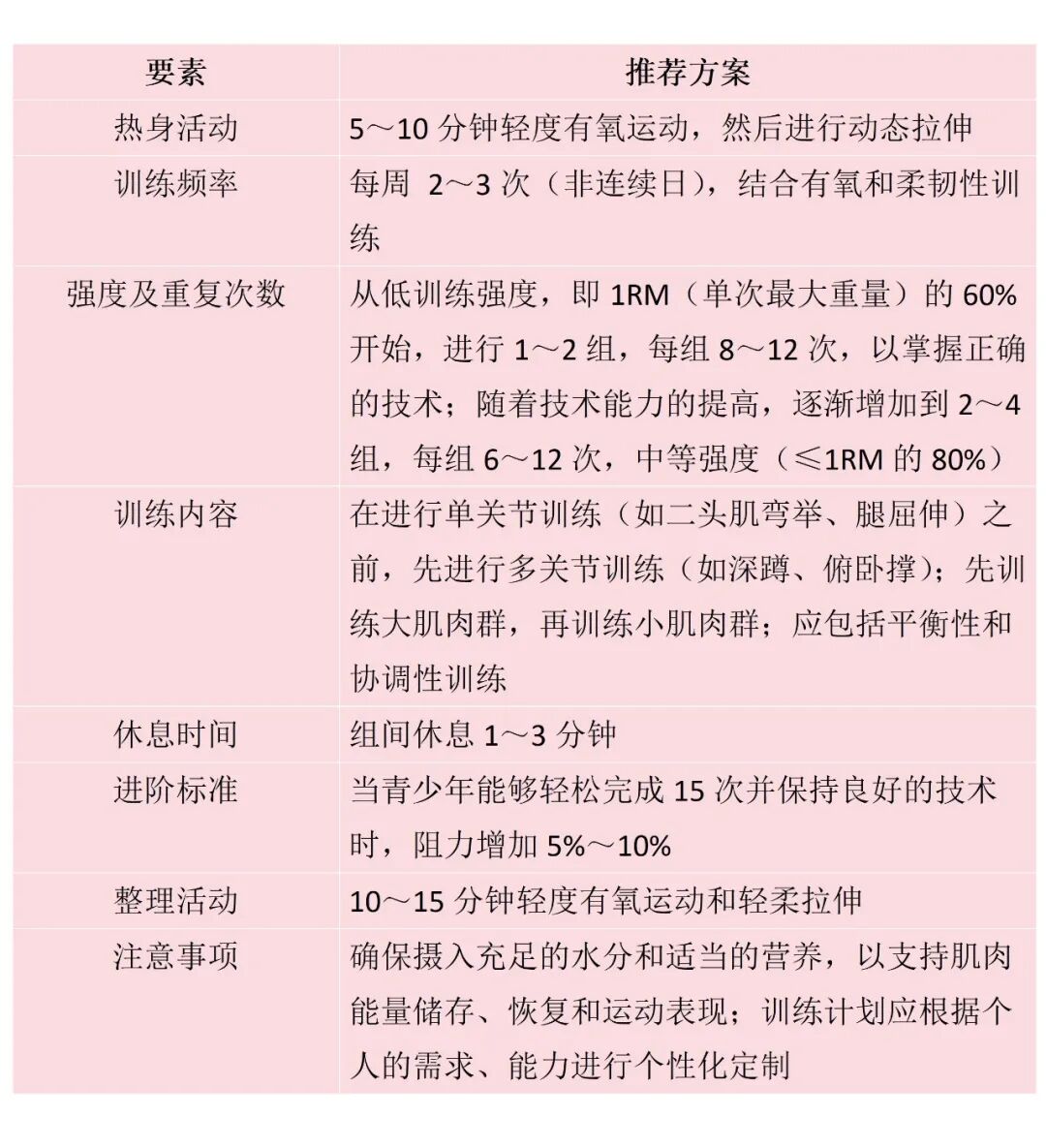
Muscle strength is an important cornerstone of health, and adolescence is a key stage in building muscle strength. Schools, parents and students should pay attention to this issue, improve the muscle strength of adolescents through scientific exercise and balanced nutrition, and lay a solid foundation for future health.